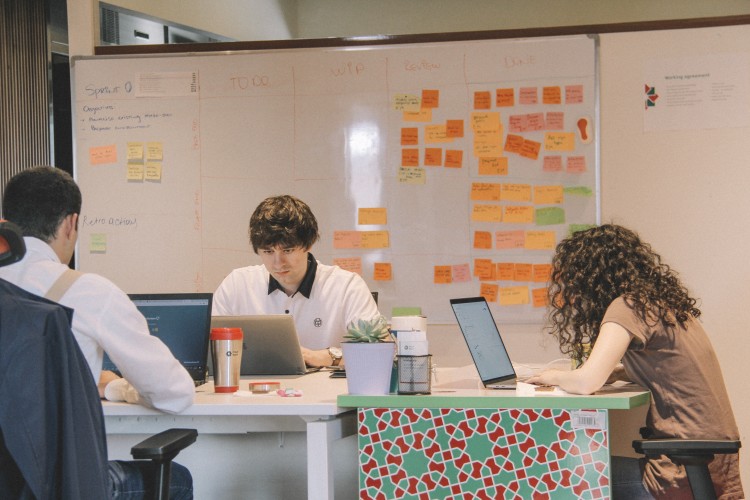
Software development methodologies determine how a software team will perform tasks, assess their work, and control the development process.
Some methodologies are lightweight, intended to guide a team with loose guidelines. Others are more rigid and only bring true value when followed to the letter.
Each methodology has its pros and cons, and finding the right one for your team can be tricky.
That’s why in today’s post, we’re going to look at the six most common software development methodologies.
1. Waterfall
Waterfall contains five phases of management: requirements, design, implementation, verification, and maintenance. Each stage requires your team to produce a deliverable before moving on to the next phase.
The waterfall method is rigid and works best for predictable projects with a clearly established goal for the final product. This means there is little need for regular client feedback or collaboration, and the development team can stay focused on one objective.
Pros
Waterfall is a simple concept to follow. The process is linear, which allows for greater focus and accessibility for newcomers.
Expectations are set before development, giving the team a clear understanding of the goal.
Great for smaller projects
Cons
Difficult to implement essential, last-minute changes
Lack of regular feedback can allow teams to stray away from the intended goal.
2. Feature-Driven Development
Feature-Driven Development is an iterative agile model which aims to develop real, well-functioning software within established deadlines. This methodology aims to make the development process as clear as possible to reduce the possibility of costly reworking in the later stages of development.
With Feature-Driven Development, the team’s to-do list guides the process. The list includes every feature that the final product requires. The team then plans, designs, and implements each stage. Each completed feature acts as a building block, coming together to build the final product.
Pros
Thanks to a clear development strategy, you can produce the final product more quickly.
Reduces the need for regular meetings
Allows development teams to break down large projects into manageable tasks
Cons
Ineffective for small projects
Lack of regular feedback from meetings can lead to late-stage confusion.

3. Agile
Regular readers of our blog will know how passionate we are about agile ways of working, but here’s a brief outline of the Agile methodology for any newcomers.
The core principle of Agile is flexibility. Agile allows development teams to make last-second adjustments based on continuous feedback from product owners, stakeholders, and end-users. Work is performed in short bursts — called “sprints” — and requires the team to regularly assess their work to optimize efficiency.
Pros
High-level collaboration between developers, stakeholders, and customers
Repeated testing reduces the risk of bugs and other issues
Frequent opportunities to assess workloads, productivity, and quality
Cons
Projects can take much longer due to regular feedback sessions and testing
Flexibility can lead to a product that is drastically different from the initial objective
It can be tough to keep documentation up-to-date
4. Scrum
Scrum offers a different way to implement Agile methodologies. It takes the core beliefs and philosophies of Agile to create a new way of working with a heavy focus on collaboration.
Like Agile, Scrum development is broken down into fixed-length iterations (see: sprints) and requires teams to be self-organized. It’s crucial to keep everyone in the loop while working with Scrum. Regular meetings such as the Daily Stand-up and sprint retrospective are essential to enable fast changes and contextual decision making.
Scrum is a more rigid methodology, with some of the disciplines of traditional software development methodologies combined with the flexibility and iterative practices of Agile.
Pros
Enables quick and cost-efficient development
You can easily keep everyone involved with the project informed
Greater visibility of work performed by an individual developer
Cons
Lack of deadlines can lead to scope creep
Daily meetings can become tedious
Not suitable for inexperienced developers

5. Extreme programming (XP)
Extreme programming — commonly referred to as XP — is another methodology that stems from Agile.
XP is based on simplicity, communication, consistent feedback, and respect. Teams should work together on every feature and develop just what is required, nothing more. This means developers will focus only on the items that will provide value to the final product, rather than worrying about the potential to include extra, unplanned features.
Pros
XP can boost employee satisfaction with regular, respectful feedback for team members.
XP produces what was specified in the original creative brief
Improves focus by forcing developers to commit to their work
Cons
XP tends to focus on the code rather than the UX
It can be challenging to make XP work with distributed teams
6. Lean
Lean is considered both a workflow methodology and a mindset. It takes principles and practices from the manufacturing industry and applies them to various other industries, including software development.
Many businesses use Lean to help them scale while still enjoying the benefits of Agile. Its basic principles allow teams to optimize their processes, reduce waste, improve knowledge, and produce quality products in a short time.
Pros
Reduces waste
Improves the ability to scale a business
Fast turnaround can give businesses that first-to-market advantage
Cons
Aggressive scheduling leaves little room for error
Can lead to worker burnout
7. Hybrid methodologies
Hybrid methodologies combine elements of different approaches to suit specific product or project requirements. One of the most popular hybrid approaches is to use Waterfall techniques for planning stages followed by an Agile approach for execution. Why should product teams hybrid methodologies? Here are the major benefits:
Benefits of hybrid methodologies
Good documentation
Product teams following the Waterfall approach use detailed documentation to stay on the right path. This covers the product’s objectives, features, and other essential details. Documentation tends to be leaner with the Agile approach but still detailed enough to guide teams.
Combining the two software development methodologies ensures that you have good documentation to rely on.
Time and cost estimates
In hybrid methodologies, time and cost estimates are reliably clear from the early planning stages. That helps teams understand the expected timeline and budgetary limitations, reducing the risk of overrunning either.
Flexibility
Embracing hybrid methodologies enables product teams to have a flexible approach to solving problems and creating the right products for the right audiences.
While the Waterfall approach focuses on linear planning and following a clear process, combining it with Agile enables product teams to be flexible. Teams following an Agile methodology need to react to feedback and implement solutions to problems that they might not have considered during the planning stages.
Encourages collaboration
Proper collaboration informs all team members of their priority tasks and shared goals. Collaborative tools make this easier than ever today, and hybrid methodologies promote working together to achieve objectives.
Issues to watch out for
Be aware of the following risks when using hybrid methodologies:
Make sure you find the right balance for your specific team and project. You may need to tweak hybrid methodologies continually to make them work.
Make sure the team is on the same page to avoid confusion and potentially costly mistakes.
You can encounter the same kinds of issues you’d face with either Agile or Waterfall methodologies. Understand the possible risks of each approach, then create a plan to mitigate them.
How to choose the right methodology for your team
Here are a few tips for choosing the right software development methodology.
1. Consider your need for flexibility
Flexibility is crucial when product requirements may fluctuate, like when user feedback is negative and you need to make big changes. But may not need as much flexibility if you’re working on a product with less uncertainty and have a clearer idea of the outcome.
2. Think about your end users
You should know what your end users are looking for before you start work on a product or feature. Using the Waterfall methodology may be enough if you have a specific group in your sights. But if you have a wider spread of users, Agile could be best.
3. Consider the size of your project
If you’re working on a large project with a huge team, you may prefer strict organization and planning to keep things organized. That makes the Waterfall approach a valuable option. However, smaller teams may prefer the Agile methodology because it’s easier for them to work together and think on their feet.
Picking a methodology that works for your team is just the beginning. As you continue your journey, you can always rely on the airfocus blog to keep you up-to-date with all the best product management tricks and tips!
Valentin Firak

Read also






Experience the new way of doing product management

Experience the new way of doing product management