Enterprise-Grade Prioritization (With Strategies and Examples for Complex Product Portfolios)

In product management, and especially when it comes to enterprises, the ability to prioritize effectively is a requirement for success.
Organizations with complex product portfolios face the issue of aligning their resources with strategic objectives, while also responding to immediate market demands. This article will take you through the world of enterprise-grade prioritization, discussing its significance, challenges, strategies, and the role of data-driven decision-making. Lets explore the path to achieving a balance between short-term business goals and long-term strategic objectives.

Introduction to enterprise-grade prioritization
Enterprise-grade prioritization is the cornerstone of managing complex product portfolios within large organizations. It goes beyond just decision-making; it's a structured approach that ensures that every resource, whether it is time, money, or manpower is invested in projects that offer the most significant returns. This prioritization process is vital for staying competitive and maximizing ROI.
What is enterprise-grade prioritization?
Enterprise-grade prioritization is the process of systematically selecting and ranking products and initiatives within a large organization, typically based on a variety of factors such as business value, customer impact, technical feasibility, and resource availability. It is a critical aspect of product management, especially for organizations with complex portfolios of products and services.
What is the significance of enterprise-grade prioritization?
Enterprise-grade prioritization helps organizations to:
Focus on the most important products and initiatives: By carefully evaluating and prioritizing all potential opportunities, organizations can ensure that their resources are invested in the areas that will have the biggest impact on the business.
Improve customer satisfaction: By focusing on products and initiatives that are most likely to meet the needs of customers, organizations can improve their customer satisfaction and retention rates.
Accelerate innovation: By prioritizing the development of new products and features, organizations can stay ahead of the competition and meet the ever-changing needs of their customers.
Improve profitability: By investing in the right products and initiatives, organizations can increase their revenue and reduce their costs, leading to improved profitability.

Understanding the challenges and complexities of prioritizing multiple products
Prioritizing multiple products and initiatives within a large organization can be a complex and challenging task. Some of the key challenges include:
Be transparent and open: It is important to be transparent and open with cross-functional teams about your prioritization decisions. Explain the reasons behind your decisions and be open to feedback. This will help to build trust and understanding between the teams.
Large number of products and initiatives: Large organizations typically have a large number of products and initiatives in the pipeline, making it difficult to prioritize them effectively.
Competing stakeholders: Different stakeholders within the organization may have different priorities, which can make it difficult to reach a consensus on which products and initiatives to focus on.
Limited resources: Organizations have limited resources, such as time, money, and people, which means that they cannot invest in all of the potential products and initiatives.
Uncertainty and change: The business environment is constantly changing, which can make it difficult to predict which products and initiatives will be successful in the long term.
Prioritization strategies and frameworks for enterprise-level product management
There are a variety of product prioritization strategies and frameworks that can be used for enterprise-level product management. Some of the most common include:
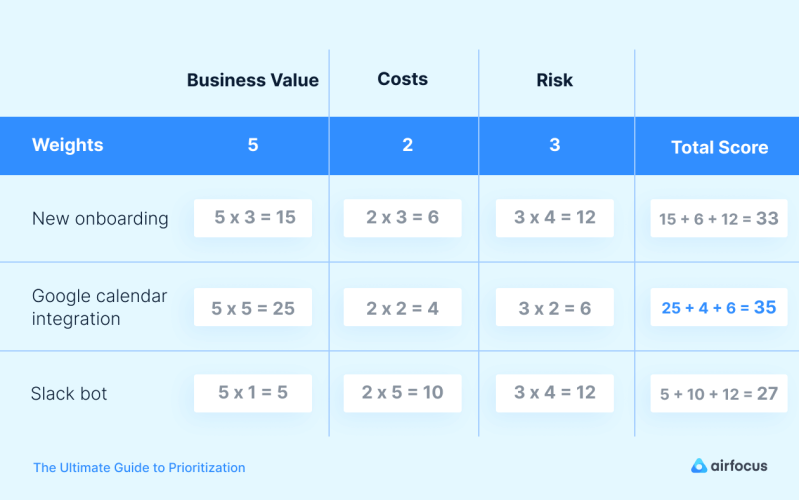
Weighted scoring
This framework assigns a weight to each prioritization factor, such as business value, customer impact, technical feasibility, and resource availability. The products and initiatives are then scored based on each factor, and the overall score is used to determine the prioritization order.
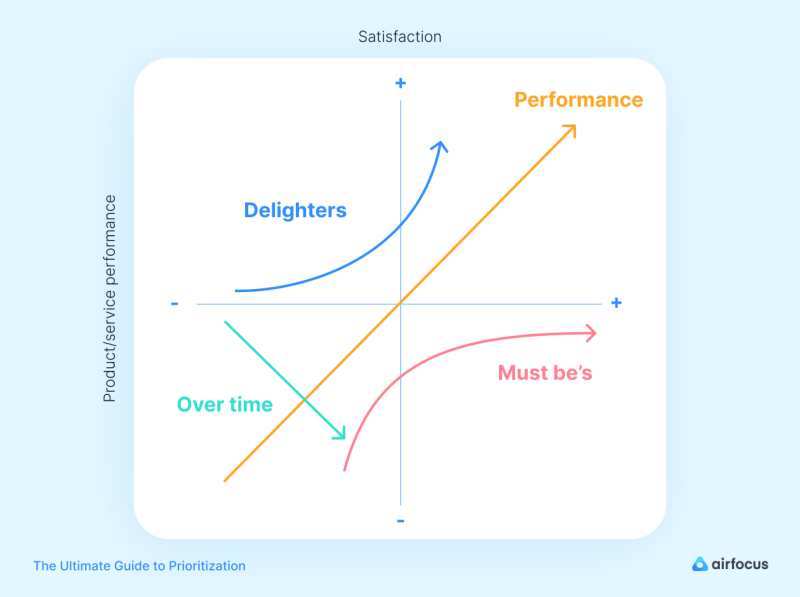
Kano model
This model classifies features into three categories: must-have, nice-to-have, and delighters. Must-have features are essential to the success of the product, and they should be prioritized over nice-to-have and delighter features.
MoSCoW method:
This method classifies requirements into four categories: must-have, should-have, could-have, and won't-have. Must-have requirements are essential to the success of the product, and they should be prioritized over should-have, could-have, and won't-have requirements.

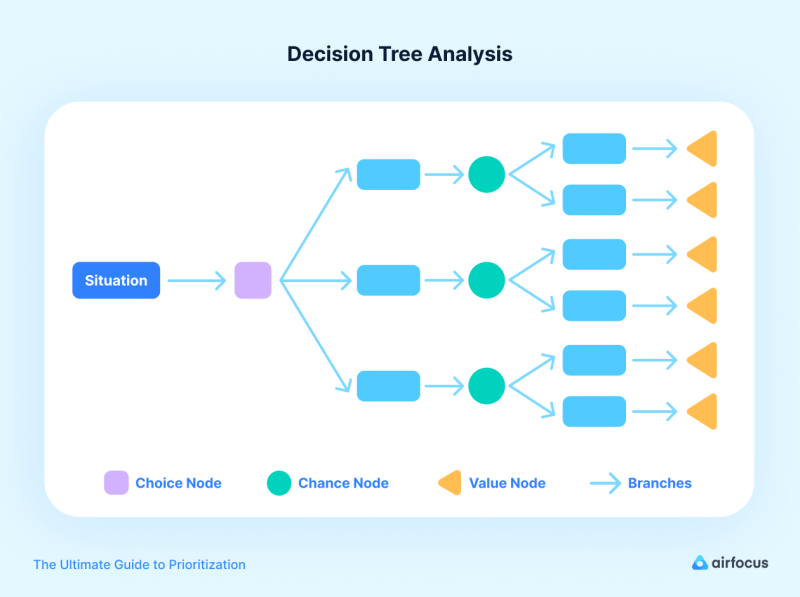
Decision tree
This framework is used to visualize the possible outcomes of different prioritization decisions. It can be used to identify the best course of action in complex situations.
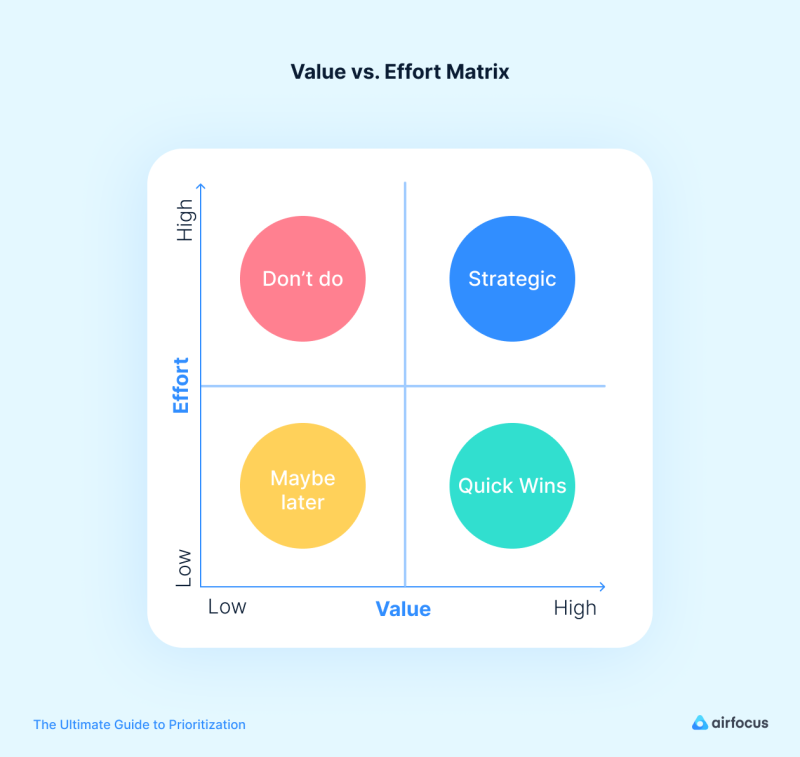
Value vs. Effort Matrix
This matrix assesses the value a feature brings to customers against the effort required to develop it. High-value, low-effort tasks are given priority, ensuring maximum impact with minimum resources. Here is a value vs. effort template that you can use.
Importance of data-driven decision-making in prioritizing projects and features
In our day and time, data reigns supreme. Enterprises must leverage data analytics and insights to make informed prioritization decisions. Data-driven decision-making is essential for effective enterprise-grade prioritization. By examining user behavior, market trends, and performance metrics, organizations can align their product development efforts with real-world demand. Organizations should collect and analyze data on a variety of factors, such as customer usage data, market research data, and financial data, to inform their prioritization decisions.
For example, organizations can use customer usage data to identify the features that are most important to customers. They can also use market research data to identify the emerging trends and opportunities in the market. Additionally, they can use financial data to assess the potential return on investment of different products and initiatives.
Balancing short-term business goals with long-term strategic objectives in the prioritization process
It is important to balance short-term business goals with long-term strategic objectives when prioritizing products and initiatives.
Organizations should prioritize products and initiatives that will help them to achieve both their short-term and long-term goals. In the current business environment, enterprises often grapple with the challenge of balancing immediate goals and long-term strategic objectives. Prioritization strategies must strike a delicate equilibrium, ensuring that short-term wins contribute to the realization of long-term vision.
For example, an organization may have a short-term goal of increasing revenue and a long-term goal of entering a new market. The organization could prioritize products and initiatives that will help them to achieve both of these goals, such as developing new features for their existing products that will appeal to new customers and developing new products that are tailored to the new market.
Collaboration and communication techniques to align cross-functional teams on prioritization
Effective prioritization requires cross-functional collaboration and clear communication. Techniques such as Agile methodologies, regular meetings, and feedback loops help teams align their efforts and keep everyone on the same page. It is important to collaborate and communicate with cross-functional teams to align on prioritization. This will help to ensure that everyone is on the same page and that the products and initiatives that are prioritized are the most important ones for the business.
Here are some tips for collaboration and communication:
Hold regular prioritization meetings
These meetings should be attended by representatives from all of the cross-functional teams that are involved in the product development process.
During the meetings, you can discuss the different products and initiatives in the pipeline and their potential impact on the business. You can also use these meetings to gather feedback from the different teams and to reach consensus on the prioritization order.
Create a shared prioritization framework
This framework should be used by all of the cross-functional teams to prioritize their work. It should be clear, concise, and easy to understand.
The framework should also be flexible enough to accommodate changes in the business environment and customer needs.
Use communication tools to stay connected
There are a variety of communication tools that can be used to stay connected with cross-functional teams, such as Slack, Microsoft Teams, and Google Chat. These tools can be used to share information, discuss priorities, and collaborate on projects.
Be transparent and open
It is important to be transparent and open with cross-functional teams about your prioritization decisions. Explain the reasons behind your decisions and be open to feedback. This will help to build trust and understanding between the teams.

Case studies of successful enterprise-grade prioritization implementations and their outcomes
There are many examples of successful enterprise-grade prioritization implementations. Here are a few:
Amazon
Amazon uses a variety of data-driven prioritization techniques to prioritize its products and initiatives.
For example, Amazon uses customer usage data to identify the features that are most important to customers and to prioritize the development of new features that customers are likely to use (e.g. “Notify me” feature that sends notification to the customer notifying them of an item’s availability).
Amazon also uses market research data to identify the emerging trends and opportunities in the market and to prioritize the development of products and initiatives that will help Amazon to capitalize on these trends.
Google uses a prioritization framework called Objective and Key Results (OKRs) to prioritize its products and initiatives. OKRs are a set of measurable goals that are aligned with the company's overall objectives.
Google teams set OKRs at the beginning of each quarter and review them at the end of the quarter to assess their progress.
Netflix
Netflix uses a prioritization framework called Prioritization by Innovation Outcome (PIO) to prioritize its products and initiatives. PIO is a data-driven framework that uses a variety of factors, such as customer usage data, market research data, and financial data, to prioritize products and initiatives based on their potential impact on the business.
Conclusion
Enterprise-grade prioritization is a critical aspect of product management, especially for organizations with complex portfolios of products and services. By following the strategies and tips outlined in this article, organizations can improve their prioritization process and make better decisions about which products and initiatives to focus on.
For more inspiration, read our full range of product management case studies.
Additional tips for enterprise-grade prioritization
Use a portfolio management tool:
A portfolio management tool can help you to track and manage your entire portfolio of products and initiatives. This can be helpful for identifying the products and initiatives that are most important to the business and for prioritizing them accordingly. You can manage your portfolio, and connect it to your roadmaps and strategy easily and in a flexible way in airfocus.
Involve stakeholders early on:
It is important to involve stakeholders early on in the prioritization process. This will help to ensure that everyone is on the same page and that the products and initiatives that are prioritized are the ones that are most important to the stakeholders.
Be flexible and adaptable:
The business environment is changing all the time, so it is important to be flexible and adaptable in your prioritization process. Be willing to change your priorities as needed to respond to changes in the market and customer needs.

Vishal Chaudhary
Read also




Prioritize with confidence
Experience the new way of doing product management



